From The Leader in Clean Power Production Technologies
Spiritwood Station Plant — North Dakota, USA
Success Story
Great River Energy (GRE)
Spiritwood, North Dakota
Plant Owner
Great River Energy (GRE)
Plant Name
Spiritwood Station
Location
Spiritwood, North Dakota
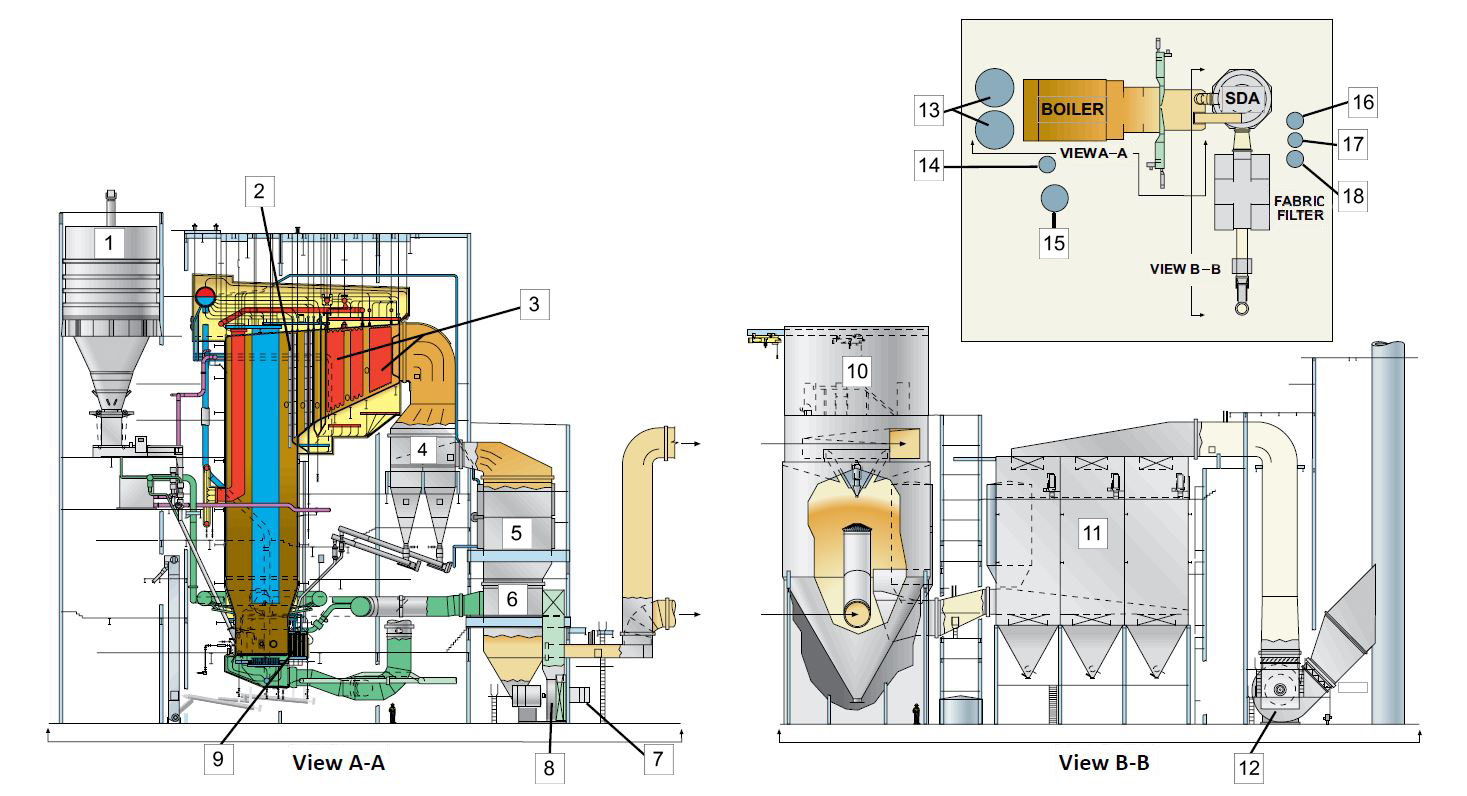
B&W Scope
Coal-fired internal recirculation circulating fluidized-bed (IR-CFB) boiler including:
- Structural steel
- Fans and motors
- Tubular air heaters
- Economizer
- Steam coil air heaters
- Steam sootblowers by Diamond Power International, Inc., a B&W subsidiary
- Multi-cyclone dust collector (MDC)
- Ash recycle/reinjection system by Allen-Sherman-Hoff, a division of Diamond Power
- Limestone injection system
- Limestone silo
- Startup burners
- Refractory lined lower furnace with erosion protection at the Reduced Diameter Zone (RDZ) transition
- Fluid bed ash coolers
- Bed drain system including screws, screeners, crusher, belt conveyor and bucket elevators
- Multi-cyclone dust collector screws
- Flues and ducts
- Segmented U-beam primary particle collectors with water-cooled support system
- Coal feeders and bunkers
- Blowdown tanks
- Instrumentation
Environmental Equipment
- Spray dryer absorber (SDA) flue gas desulfurization system
- Pulse jet fabric filter
- Selective non-catalytic reduction (SNCR) system including ammonia storage
Boiler Specifications
- Boiler type: Internal Recirculation CFB design
- Design fuel: Lignite coal
- Startup fuel: Natural gas
- Capacity: 275 MWt (90 MWe net plus process steam)
- Steam flow: 805,000 lb/h (101.4 kg/s)
- Steam pressure:1780 psig (12.3 MPa)
- Steam temperature: 1006F (541C)
Contract Order: 2008
Commercial Operation: 2012
Project/Boiler Facts
- Combined heat and power plant will provide process steam for an adjacent malt plant and will normally generate approximately 56 MW net of electricity for the regional transmission grid. MW output is dependent upon how much steam is consumed by the steam host.
- The addition of limestone to the circulating bed reduces SO2 emissions from the boiler.
- Low furnace temperatures and staged combustion limit NOx emissions.
- Unique two-stage solids collection system using U-beams and MDC provides superior collection efficiency. The recycling of solids collected by the MDC improves combustion efficiency and limestone utilization.
- The U-Beam and MDC solids collection system requires significantly less maintenance than hot cyclones.
- RDZ design with silicon carbide tiles at the top edge of the furnace refractory is used to minimize tube erosion at the interface.