Search Results
Numerical Modeling in Power Plant Applications - An Overview
Continuous and steady advances in computer technology have changed the way engineering design and analyses are performed. These advances allow engineers to manage larger-scale problems and more complex systems, or to look in more detail at a specific process. Using advanced computer technology to perform engineering analysis, numerical modeling has emerged as an important field in engineering.
View Web PageThe Importance of Construction Technology
Technological advances including computer-aided design, global positioning systems, laser scanning systems, and more powerful lift cranes have enabled construction engineers and technicians to support supervision by refining the planning process and expediting the work in the field.
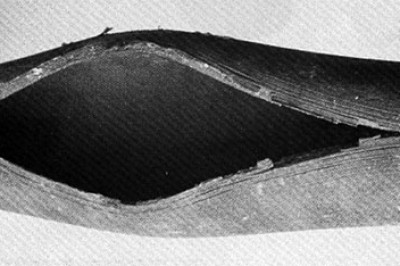
View Web PageFinding the Root Cause of Boiler Tube Failures
Identifying and correcting the root cause of tube failures is essential to help lessen the chance of future problems. A comprehensive assessment is the most effective method of determining the root cause of a failure. A tube failure is usually a symptom of other problems.
View Web PageConstruction Planning and Scheduling
Typical participants include the project manager, scheduler/planner, project superintendent(s), construction engineer(s), and other contributors as selected by the project manager. The basis for this planning session is the scope of work as originally defined and estimated, and the existing conditions of the construction site.
Part I - Specifying a Steam Generator
The basic design is derived from the functional requirements of the application. The equipment designer needs to know the key characteristics of all major system inputs and all performance output requirements. This information is essential for setting vital system design parameters such as size, capacity, materials, equipment redundancy level, etc.
View Web PageBoiler Operations That Affect Efficiency (Part 2)
Adjustments can typically vary the turbulence and flow rates in burners. Increased turbulence increases the air-fuel mixing. It also increases the combustion intensity, provides faster heat release, reduces unburned carbon (UBC) in the ash, permits operation with less excess air, and increases boiler efficiency.
View Web Page