Wet Scrubber - Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD)
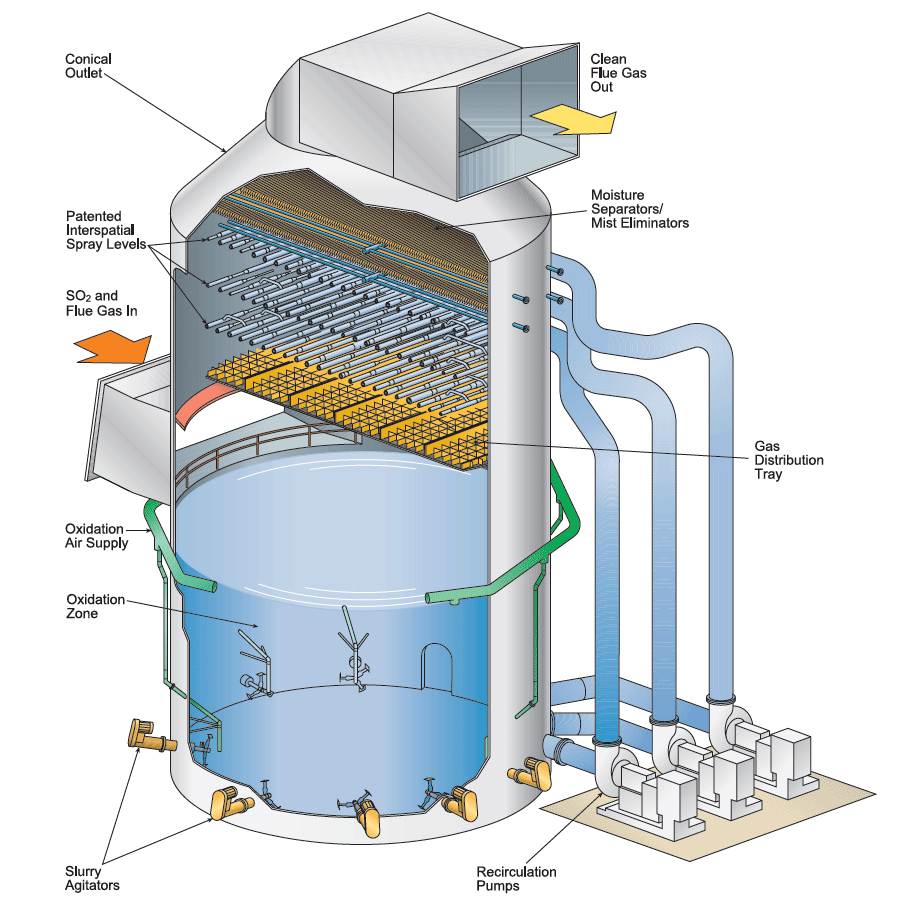 B&W’s proven technology, flexibility of design options and advanced features of our wet flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems help to reduce emissions in new or retrofit applications.
B&W’s proven technology, flexibility of design options and advanced features of our wet flue gas desulfurization (FGD) systems help to reduce emissions in new or retrofit applications.
Our wet FGD systems, or wet scrubbers, have operated efficiently, economically and reliably since 1971.
Current designs can achieve more than 99% SO2 removal, with system availability greater than 99.5%. Our absorber design also provides reduced operating and maintenance costs.
As a multi-pollutant control device, B&W’s wet scrubbers also help control filterable (solid) particulate, acid mist and mercury.
Features and benefits include:
- Forced or inhibited oxidation – provide options for selling gypsum byproduct or eliminating wastewater discharge
- Single or dual tray designs – promotes gas/liquid contact and uniform gas distribution for improved emissions reduction
- Large, single absorber capability to treat multiple boilers – smaller plant footprint and reduced operating costs
- Choice of reagents – provides flexibility
- Interspatial spray headers – more effective overlapping spray coverage for shorter absorber towers, reduced pump power, lower building height, less external recirculation piping, and easier nozzle inspection and maintenance
- Moisture separators – rugged and effective design helps prevent slurry carryover
In addition to flue gas absorbers, we supply complete systems, including reagent preparation, dewatering and related system equipment. Our wet FGD experts provide design and engineering as well as start-up, commissioning and support services.
Current B&W designs are achieving 99% SO2 removal with system availability greater than 99.5%
Applicable boiler sizes:
- 50 MW to 1300 MW
Removal efficiencies:
- Up to 99%
Reagents:
- Primarily limestone; also lime, magnesium-enhanced lime, sodium carbonate, and ammonia.
Fuels:
- All solid fuels — primarily coal.
